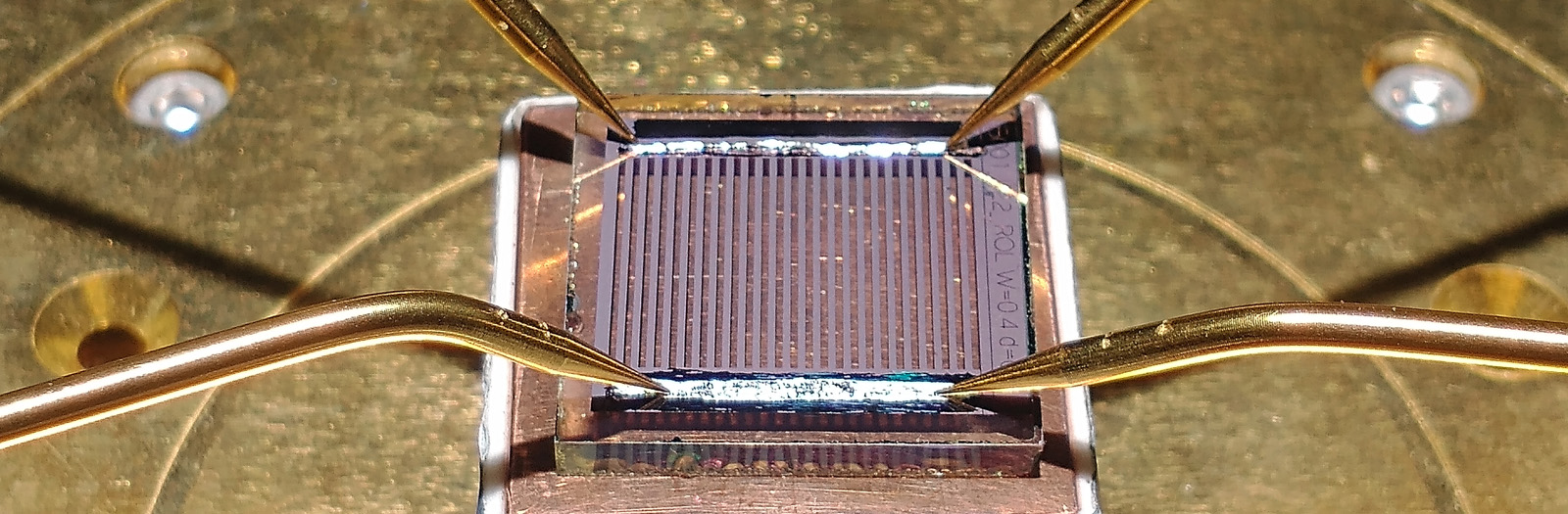
Hi-BITS
Standard CIGS solar cells use molybdenum as the back electrode and achieve 23% efficiency. However, to exceed this limit, thus approaching the Schockley-Queisser limit, a paradigm shift and an alternative cell structure are proposed.
The aim of the Hi-BITS project is to develop a CIGS-based solar cell architecture with a transparent rear electrode that could replace molybdenum in the future.
The electrode's transparency in the visible and near-infrared wavelengths guarantees the absorption of sunlight from both sides of the cell, further increasing its maximum efficiency. This will also open up new application possibilities for CIGS technology. Passivation of this contact will also reduce the thickness of the absorption layer, reducing production cycle time and material consumption.
The new cell structure will then be implemented in four different photovoltaic module prototypes: bifacial modules, modules with an integrated rear reflector layer, semi-transparent modules, and tandem modules. The prototypes will be tested outdoors in four different locations across Europe.
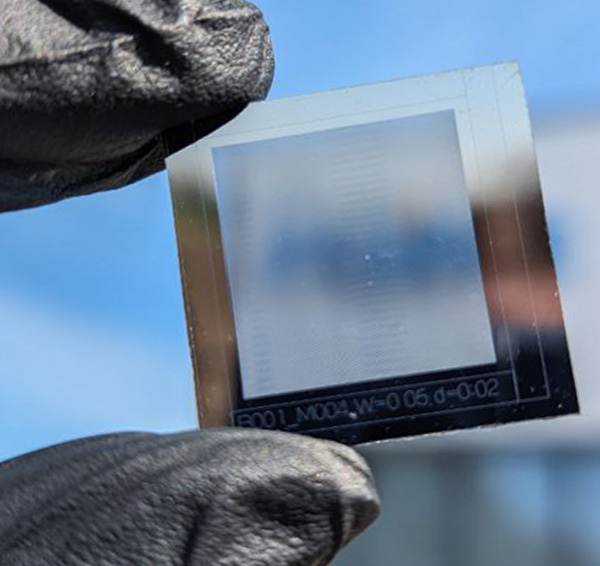

Roltec's tasks within the Hi-BITS Project:
- laser structuring of prototype solar modules and cells,
- encapsulation of prototype modules,
- creation of a semi-transparent solar cell (Roltec is the leader of the project),
examination of the compliance of modules with EU standards and directives (Roltec is the task leader).
Additionally, Roltec is responsible for developing a compliance report for prototype modules with selected EU standards and regulations in the context of several selected applications, including building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and agrophotovoltaics.
More information on the project home page .
The Hi-BITS project in numbers:
Project partners:
- International Iberian Nanotechnology Laboratory ( INL )
- French National Center for Scientific Research ( CNRS )
- Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden‑W ü rttemberg ( ZSW )
- Uppsala University ( UU )
- Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology ( EMPA )
- University of Luxembourg ( uni.lu )
- Catalonia Institute for Energy Research ( IREC )
- Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg ( MLU )
- Midsummer AB ( MIDS )
- Sunplugged – Solare Energiesysteme GmbH ( SUN )
- GreenDelta GmbH ( GDL )
- Saint Gobain Research ( SG )
- Avancis GmbH ( AVA )


Funded by the European Union. Programme: HORIZON EUROPE ; project ID: 101122203.
The views and opinions expressed are solely those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Union. Neither the European Union nor the awarding authority can be held responsible for them.

